Realmカテゴリー記事の一覧です
【Android Kotlin】MVVM+DataBinding+LiveData+ Coroutine+Flow サンプル
Android, Androidstudio, Kotlin, PC, Realm, Windows, 紹介
前回、DataBindingについて解説させていただきましたが、その際にfindViewByIdよりもDataBindingが推奨されているという内容を記載しました。
それと同じように、使っていた技術よりも推奨されるものが出てきたり、新しい考え方であったり、アプリ開発をより効率的に行えるような、便利な機能がどんどん登場しています。
そこで今回は、以前作成したアプリを便利な機能を使って改良し、そこで使ったいくつかの機能について、それぞれ解説していきたいと思います。
アプリの変更点
今回は、前々回のブログで紹介したRealmにデータを保存してそれを表示するアプリに修正を加えたものを使って解説しますので、まずはどのよう変更点があるかコードを見ながら説明します。
修正前のアプリの詳しい内容についてはブログで紹介していますので、まだ見ていないという方はそちらもご覧ください。
機能の追加
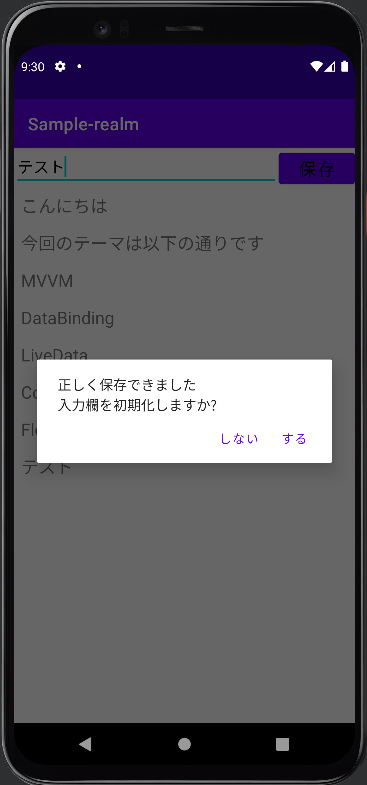
アプリの機能自体は修正前とほとんど変わらず、データをrealmに保存して、保存した内容を表示するものですが、新しい機能として「保存」ボタンを押した後に入力したテキストを消去するかどうかの選択肢を表示するようにしました。
MainActivity.kt
まずはMainActivityの変更点から紹介します。
大きく変わった点として、findViewByIdを使用していた箇所をDataBindingに変えてレイアウトと連携させています。
加えて、今回新しく追加した「保存」ボタンを押した後の表示といった各種イベントの登録を行っています。
package com.example.sample_realm
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.activity.viewModels
import androidx.appcompat.app.AlertDialog
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import com.example.sample_realm.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
private val viewModel: SampleViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// レイアウトファイルへ
// viewModel(this@MainActivity.viewModel)と
// lifecycleOwner(this@MainActivity)を
// (binding = it)連携させる
ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater).apply {
viewModel = this@MainActivity.viewModel
lifecycleOwner = this@MainActivity
}.let {
binding = it
viewModel.binding = it
setContentView(it.root)
// アダプターインスタンス作成
viewModel.sampleAdapter = SampleListAdapter(
inflater = layoutInflater
)
// レイアウトファイルのid/sampleListへ連携させる
it.sampleList.adapter = viewModel.sampleAdapter
}
// Realのイベント設定
viewModel.setRealmEvents()
// layoutファイル 各種イベント登録
collectFlow()
}
// layoutファイル 各種イベント登録
private fun collectFlow() {
viewModel.apply {
lifecycleScope.launchWhenStarted {
clickWriteFlow.collect {
AlertDialog.Builder(this@MainActivity)
.setCancelable(false)
.setMessage("正しく保存できました\n入力欄を初期化しますか?")
.setNegativeButton("しない") { _, _ ->
// No処理
}
.setPositiveButton("する") { _, _ ->
// Yes処理
liveDataTextLd.value = ""
}
.show()
}
}
}
}
}
SampleListAdapter.kt
ListAdapterで大きな変更点は特にありませんが、以前はこの中にあったViewHolderがなくなって、新しくViewHolderのクラスを作って独立させています。
package com.example.sample_realm
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.ViewGroup
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
import com.example.sample_realm.databinding.ItemSampleBinding
class SampleListAdapter(
private val inflater: LayoutInflater
) : RecyclerView.Adapter<RecyclerView.ViewHolder>() {
private val sampleList = mutableListOf<String>()
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): SampleViewHolder =
SampleViewHolder.create(inflater, parent, false)
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: RecyclerView.ViewHolder, position: Int) {
(holder as SampleViewHolder).bind(sampleList[position])
}
override fun getItemCount(): Int = sampleList.size
fun updateSampleList(sampleList: List<String>) {
// 一度クリアしてから新しいメモに入れ替える
this.sampleList.clear()
this.sampleList.addAll(sampleList)
// データに変更があったことをadapterに通知
notifyDataSetChanged()
}
}
SampleViewHolder.kt
ViewHolderは先述の通り、ListAdapterの中に含めていたものを新しいクラスとして作成しています。
記述してある処理自体は大きく変わっていませんが、DataBindingに合わせて記述の仕方が変わっています。
package com.example.sample_realm
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.ViewGroup
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
import com.example.sample_realm.databinding.ItemSampleBinding
class SampleViewHolder private constructor(
private val binding: ItemSampleBinding
) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root) {
companion object {
fun create(
inflater: LayoutInflater,
parent: ViewGroup,
attachToRoot: Boolean
) = SampleViewHolder(
ItemSampleBinding.inflate(
inflater,
parent,
attachToRoot
)
)
}
fun bind(
sample: String
) {
binding.sampleTextView.text = sample
}
}
SampleViewModel.kt
修正にあたって、新しく作成されたクラスになります。後述するMVVMの設計モデルに則ってRealm関係の処理やクリックした際の処理を記述しています。また、Coroutineとしての処理を記載し、API通信などを追加できるようにしたり、変数に値をセットしたりしています。
package com.example.sample_realm
import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope
import com.example.sample_realm.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
import io.realm.Realm
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableSharedFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class SampleViewModel: ViewModel() {
lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
lateinit var sampleAdapter: SampleListAdapter
private val realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance()
// LdプレフィックスでLiveDataと分かるように記載
val liveDataTextLd = MutableLiveData<String>()
// FlowプレフィックスでSharedFlowと分かるように記載
val clickWriteFlow = MutableSharedFlow<Unit>()
// イニシャライズ
init {
initInputInfoData()
}
private fun initInputInfoData() {
// コルーチンとして処理開始
viewModelScope.launch {
runCatching {
// API 通信などここでTry
}.onSuccess {
// set data
liveDataTextLd.value = ""
}.onFailure {
// エラー
}.also {
// 後処理
}
}
}
// 書込みボタンクリックイベント
fun onClickWrite() {
val text = liveDataTextLd.value.toString()
//テキストが空の場合には無視をする
// if (value.isEmpty()) return
if (text.isEmpty()) return
viewModelScope.launch {
// putData(liveDataTextLd.value.toString())
putData(text)
clickWriteFlow.emit(value = Unit)
}
}
private fun putData(value: String) {
//テキストが空の場合には無視をする
// if (value.isEmpty()) return
// Realmのトランザクション
realm.executeTransactionAsync {
//DataListのオブジェクト作成
val data = it.createObject(DataList::class.java)
//nameに先ほど入力されたtextを入れる
data.name = value
//データの上書きをする
it.copyFromRealm(data)
}
}
fun setRealmEvents() {
// DBに変更があった時に通知が来る
realm.addChangeListener { it ->
//変更があった時にリストをアップデートする
val list = it.where(DataList::class.java).findAll().map { it.name }
//UIスレッドで更新する
binding.sampleList.post {
sampleAdapter.updateSampleList(list)
}
}
// 初回表示の時にメモ一覧を表示
realm.executeTransactionAsync {
val list = it.where(DataList::class.java).findAll().map { it.name }
// UIスレッドで更新する
binding.sampleList.post {
sampleAdapter.updateSampleList(list)
}
}
}
}
activity_main.xml
DataBindingをつかってViewModelと結びついています。これによって、EditTextに入力されたデータがViewModelのLiveDataでも使用可能になったり、ViewModelのメソッドにアクセスできるようになっています。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
<variable
name="viewModel"
type="com.example.sample_realm.SampleViewModel" />
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/sample_edit_text"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="テキストを入力してください"
android:text="@={viewModel.liveDataTextLd}"
android:textColor="#000000"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/add_button"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/add_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="保存"
android:onClick="@{() -> viewModel.onClickWrite()}"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:iconTint="#000000"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/sampleList"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layoutManager="androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/sample_edit_text" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>
使った機能や設計モデルの紹介
コードを見ながらどのような変更があったのか、というのを簡単に説明しましたので、続いてはそこで使った機能や設計モデルについて詳しく紹介していきたいと思います。
MVVM
ViewModelの説明にあったように、MVVMの設計モデルを使った形に変えています。
MVVMはModel, View, ViewModelの頭文字をとったもので、MVCから派生した設計モデルになります。
MVCと同じ部分もありますが、MVVMのそれぞれについて解説していきます。
Model
Modelに関しては、MVCと同じくシステムの中のビジネスロジックを担当している部分になります。データの処理を行って、データの変更をViewに通知したりします。
View
ViewもMVCと同じ役割で、Modelが扱っているデータを取り出して、UIへの出力などを行っています。
View Model
ViewModelはViewとModel間の伝達や、状態の保持を担当します。
今回のサンプルでは、新しくViewModelのクラスを作成し、それぞれとデータのやり取りを行っています。
DataBinding, LiveData
DataBindingは前回のブログで紹介しましたが、その際は外部からViewの表示を変えることができるという単方向のみの説明でした。しかし、DataBindingには双方向でのデータのやり取りをする機能もあります。
双方向の場合は例にあるように “@={viewModel.liveDataTextLd}” という様に@の次に “=” を入力する必要があります。これによって、Viewからもデータを送るということが可能になります。
また、その際に LiveData というデータを監視するクラスを使用することで、テキスト入力欄に変更があるたびに、自動でデータの更新を行ってくれます。
Coroutine
Coroutineは非同期処理を簡略化することができるデザインパターンのことです。
今回の例では、非同期処理をする必要がほとんどありませんでしたが、コードを紹介していた時にも触れたように、メインの機能と合わせて、API通信をする時等に使用すると非常に役立つものになっています。
Flow
Flowは先ほど紹介した Coroutine の一種であり、サンプルでは MutableSharedFlow として実装されていたものになります。今まで使われていたRxと同じような動きをすることが可能で、複数の値を順次出力できるため、データベースからリアルタイムで更新情報を受け取る際などに便利な機能です。
サンプルではクリックされた際に、MainActivityのイベント登録処理にデータを渡しています。
まとめ
いかがでしたでしょうか。説明を読んだだけでは理解が難しい部分もあると思いますが、自分でそれぞれの機能を使ってみるとより理解が深まりますので、アプリ開発の際にはぜひ活用してみてください。
【Kotlin】
Realmにデータを
保存する方法を解説!
Android, Androidstudio, Kotlin, PC, Realm, Windows, 紹介
以前の記事で、Realmに入ったデータを取得する方法について解説しました。
その時の説明では、既にデータを用意しているという前提で話を進めていましたが、実際にアプリを開発するとなると、こちらからデータを取得するだけでなく、データを保存できるようにしたいという場合もあると思います。
なので、今回はKotlinでRealmを使う方法と、Realmにデータを保存、Realmに保存したデータを表示する方法について例を交えながら解説していきたいと思います。
今回は例として使っているRealmのバージョンは 10.11.0 ですので、ご注意ください。
サンプルアプリの紹介
今回の解説で使用するサンプルアプリはこちらになります。
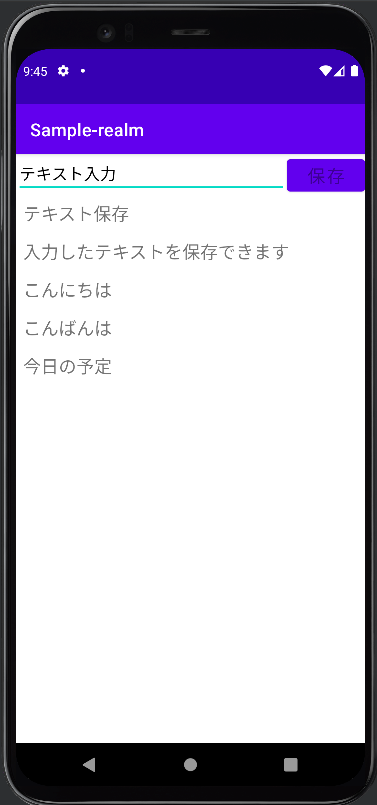
入力したテキストをRealmに保存し、保存した内容を画面に表示するという機能を持っています。
今回はこのサンプルをもとに解説をしていきたいと思います。
サンプルアプリの作成
プロジェクトの作成
まずはサンプルのアプリを作るためのプロジェクトを作成します。最初に選ぶプロジェクトは何でも大丈夫ですが、今回は Empty Activity を選択しました。名前は「Sample-realm」としています。
Realmの導入
プロジェクトの作成が完了したら、Realmを導入して使えるようにします。
まずは、”build.gradle(アプリ名)” を開いてください。
既に数行記載がありますが、一番上に以下のコードを記述します。
// build.gradle(Sample-realm)
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
// 以下のbuildscriptを記述
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath "io.realm:realm-gradle-plugin:10.11.0"
}
}
これでRealmのプラグインを追加しています。バージョンはその時によって変わるので、適宜確認してください。
続いては、”build.gradle(:app)” と書かれたファイルを開いてください。その一番上にpluginsと書かれた箇所があると思います。そこに以下のコードを記述します。
// build.gradle(:app)
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.android'
// 以下のコードを記述
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.kapt'
}
//以下のコードを記述
apply plugin: "realm-android"
すると画面の上部にSync nowという表示が出てくると思いますので、そちらを押してください。
Realmの初期化
Realmの導入は完了しましたので、続いてはRealmの初期化を行っていきます。
Applicationクラスの追加
まずは、Applicationクラスを追加したいので、MainActivityと同じ階層に○○Application(サンプルはSampleApplication)というクラスを作成します。作成したら、中身を編集していきます。
まずは、Realmを使えるように以下のコードを記述してください
// SampleApplication.kt
package jp.co.chrono.sample_realm
import android.app.Application
import io.realm.Realm
class SampleApplication: Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
Realm.init(this) //Realmの初期化
}
}
ここではRealmが使えるようにimportと、onCreate()の中でRealmを初期化しています。
Manifestに記述
Applicationの作成が完了したら、それを “AndroidManifest.xml” に追加します。
applicationタグの中に android:name=”Application名” を記述してください
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:name="jp.co.chrono.sample_realm.SampleApplication"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Samplerealm"
tools:targetApi="31">
この記述でアプリのApplicationクラスがSampleApplicationになります。
これでRealmの初期化も完了です。
レイアウトの設定
続いては、画面に表示するレイアウトの実装をしていきます。ただ、今回の趣旨とは少し離れるので、細かい解説等は省略します。
リストの作り方については、以前のブログでも紹介していますので、気になった方はそちらも参考にしてください。
RecycleViewの追加
今回は、表示する内容がリストになっているので、RecycleViewを使いたいと思います。
まずは、 “build.gradle(:app)” を開いて、dependenciesの中に以下のコードを記述してください。
dependencies {
implementation 'androidx.core:core-ktx:1.7.0'
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.5.1'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.7.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.1.4'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.13.2'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.3'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.4.0'
//この一行を追加
implementation 'androidx.recyclerview:recyclerview:1.2.1'
}
ここでSync Nowが表示されたら、そちらも押してください。
画面のレイアウト
つづいては、画面のレイアウトを設定するので、activity_mainを開き、以下の通りにコードを記述します。細かい設定に関しては自由に決めてしまっても問題ありません。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="jp.co.chrono.sample_realm.MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/sample_edit_text"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="テキスト入力"
android:textColor="#000000"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/add_button"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/add_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="保存"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:iconTint="#000000"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/sample_list"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layoutManager="androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/sample_edit_text" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
続いて、リストを表示する新しいファイル(サンプルはitem_sample.xml)を作成し、以下のコードを記述してください。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/sample_text_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="8dp"
android:textSize="20sp" />
これでレイアウトの実装は完了です。
Adapterの実装
続いて、Adapterの実装をするため、Adapterのクラス(サンプルではSampleListAdapter.kt)を作成してください。
作成できたら、以下のコードを記述します。
package jp.co.chrono.sample_realm
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.TextView
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
import com.example.sample_realm.R
class SampleListAdapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<SampleListAdapter.SampleViewHolder>() {
private val sampleList = mutableListOf<String>()
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): SampleViewHolder {
val view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.context).inflate(R.layout.item_sample, parent, false)
return SampleViewHolder(view)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: SampleViewHolder, position: Int) {
holder.bind(sampleList[position])
}
override fun getItemCount(): Int = sampleList.size
fun updateSampleList(sampleList: List<String>) {
// 一度クリアしてから新しいメモに入れ替える
this.sampleList.clear()
this.sampleList.addAll(sampleList)
// データに変更があったことをadapterに通知
notifyDataSetChanged()
}
class SampleViewHolder(view: View): RecyclerView.ViewHolder(view) {
fun bind(sample: String) {
val textView = itemView.findViewById<TextView>(R.id.sample_text_view)
textView.text = sample
}
}
}
この中では、onBindViewHolder()の中でSampleViewHolderのbind()を呼び出し、TextViewに文字列を入れています。
Adapterが作成できたので、これをRecyclerViewにセットします。
セットするには “MainActivity.kt” の中に以下のようにコードを記述します。
package jp.co.chrono.sample_realm
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.EditText
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
import com.example.sample_realm.R
import io.realm.Realm
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var adapter: SampleListAdapter
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val recyclerView = findViewById<RecyclerView>(R.id.sample_list)
adapter = SampleListAdapter()
recyclerView.adapter = adapter
SampleListAdapterのadapterを定義して、それをonCreate()の中で代入しています。
その後、findViewById()で sample_list を取得してadapterに代入しています。
これでレイアウトの設定も完了です。
Realmとの連携
それでは、今回の本題であるRealmとの連携方法について解説していきます。
まずは、テキストを保存するためのデータ形式を定義するための、クラス(サンプルではDataList.kt)を作成してください。
中身は以下のコードを記述して下さい。
package jp.co.chrono.sample_realm
import io.realm.RealmObject
open class DataList: RealmObject() {
var name: String = ""
}
今回は、保存する内容がテキストだけなので、nameのみの記述になっています。
そして、ここで重要な点が RealmObjectを継承している点と、open修飾子を付ける点になります。この二つはどちらもRealmライブラリの中で処理をするために必要な記述なので、Realmを使う際は忘れないようにしましょう。
データ形式の定義ができたら、文字列が入力された状態で保存ボタンを押すと画面に表示される機能を実装していきます。
MainActivity.ktをを開き、先ほどの記述の下に新しくコードを記述してください。
val editText = findViewById<EditText>(R.id.sample_edit_text)
val addButton = findViewById<Button>(R.id.add_button)
val realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance()
addButton.setOnClickListener {
val text = editText.text.toString()
if (text.isEmpty()) {
//テキストが空の場合には無視をする
return@setOnClickListener
}
// Realmのトランザクション
realm.executeTransactionAsync {
//DataListのオブジェクト作成
val data = it.createObject(DataList::class.java)
//nameに先ほど入力されたtextを入れる
data.name = text
//データの上書きをする
it.copyFromRealm(data)
}
//テキスト入力欄を空にする
editText.text.clear()
}
内容について解説していきます。
まずは1,2行目では findViewById を使って EditText と Button のViewを取得しています。
4行目ではRealmのインスタンスを取得しています。この記述はRealmの操作を行うときには必ず記述しないといけないので、これも忘れないように注意しましょう。
6から24行目はボタンを押したときの処理を記述しています。
空のテキストを保存しないように、最初に文字列が入っているかのチェックをしています。文字列が入力されている時は次の realm.executeTransactionAsync() の処理に進みます。
そこではまず、DataListのオブジェクトを作成します。この時、同時にRealmのDBにも登録がされます。
その後、オブジェクトに入力された文字列を代入し、copyFromRealm() でデータを上書きしています。
これで、文字列をDBに登録することができます。
その後の editText.text.clear は次の内容を入力しやすいように、テキスト入力欄を空にしています。
以上の内容が記述できたら、その下にまた以下のコードを記述します。
// DBに変更があった時に通知が来る
realm.addChangeListener {
//変更があった時にリストをアップデートする
val sampleList = it.where(DataList::class.java).findAll().map { it.name }
//UIスレッドで更新する
recyclerView.post {
adapter.updateSampleList(sampleList)
}
}
// 初回表示の時にメモ一覧を表示
realm.executeTransactionAsync {
val sampleList = it.where(DataList::class.java).findAll().map { it.name }
// UIスレッドで更新する
recyclerView.post {
adapter.updateSampleList(sampleList)
}
}
}
}
この記述は二つに分かれていますが、どちらもAdapterの updateSampleLIst() を呼び出しています。
一つ目は、DBに変更があった際に表示しているリストを更新しています。
しかし、それだけだとアプリを起動した時に何も表示されないので、初回表示の時にもDBの内容を表示するようにしています。
詳しい内容としては、where().findAll() を使って、DBに登録されているDataListを取得し、それを引数にして updateSampleList() を呼び出しています。
アプリの完成
以上でサンプルアプリの作成は完了です。
実際に触ってみると、入力したテキストを保存できていることが確認できると思います。

まとめ
いかがでしたでしょうか。今回は基本的な内容の解説になりましたが、今後もRealmを使う機会は増えてくると思いますので、入門としてぜひ参考にしてみてください
【Kotlin】
保存されたデータを
取得する方法!
【realm】
Android, Androidstudio, Kotlin, Realm, 紹介
realmはスマートフォンやタブレットなどのモバイル向けのデータベースです。
軽量かつ高速であり、実装が容易という特徴も持っています。
また、RealmはKotlinにも対応しているため、Androidのアプリ開発をする際に使っているという方も多いと思います。
そんな中で、realmに保存したデータを取得したい、入っている内容を確認したいという場面があると思います。
そこで今回は、kotlinでrealmのデータを取得する方法を解説したいと思います。
データの用意
前提としてこのようなDBモデルと、以下のデータが入っているとします。
open class Sample : RealmObject() {
@PrimaryKey
var id: Int = 0
@Required
var text: String = ""
}
| id | text |
| 1 | Sample1:おはようございます! |
| 2 | Sample2:こんにちは! |
| 3 | Sample3:こんばんは! |
realmからデータを取得する方法
では実際にrealmに保存されたデータを取得する方法を解説します。
取得する方法
以下の方法でデータを取得することができます。
findAll() を使うとすべてのデータ、findFirst() を使うと最初の一つだけのデータを取り出すことができます。
//Realmのインスタンスを取得する
val realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance()
//Realmからすべてのデータを取得する
val results = realm.where(Sample::class.java).findAll()
//Realmから最初のデータを取得する
val result = realm.where(Sample::class.java).findFirst()
//取得したデータをlogに出力
Log.e("realm", "$results")
Log.e("realm", "$result")
//Realmオブジェクトを削除する
realm.close()
データをログに出力させれば、どういった内容が保存されているのかすぐに確認できますので、状況に合わせて追加してみてください。
//Logcatの出力例
//findAll()
Sample = proxy[{id:1},{text:Sample1:おはようございます!}],
Sample = proxy[{id:2},{Sample2:こんにちは!}],
Sample = proxy[{id:3},{text:Sample3:こんばんは!}]
//findFirst
Sample = proxy[{id:1},{text:Sample1:おはようございます!}]
検索で使える条件
上記の例では、データを取得する際にfindAll()とfindFirst()を使って取得するデータの数を変えていました。
それに加えて他の条件を追加することで、特定のデータのみを取り出すということもできます。
今回はその条件コードの中でも使う頻度の高いと思ったものを選んで紹介します
・.equalTo(“フィールド名”, 値)
フィールド名が一致したデータを抽出する
・.greaterThan(“フィールド名”, 値)
指定したフィールド名の値が、条件より大きいデータを抽出する
・.lessThan(“フィールド名”, 値)
指定したフィールド名の値が、条件より小さいデータを抽出する
・.contains(“フィールド名”, “値”)
指定した値を含むデータを抽出する
これらを使えばより効率的にデータを取得することができますので、場合に合わせて使ってみてください。
まとめ
いかがでしたでしょうか。今後もrealmを使う機会は多いと思いますので、知らなかった方はこれを機に学んでみてはいかがでしょうか。
もう既に知っているという方も、復習としてぜひ参考にしていただければと思います。